Your dentist Božidar Ilić, a resident at the Oral Surgery Department at the Faculty of Dental Medicine in Belgrade, answers the most frequently asked questions about dental bridges, crowns and veneers.
What are dental bridges?
Dental bridges or veneers consist of two or more crowns fixed to the teeth on either side of the gap created by a missing tooth. The teeth adjoining the gap made by a missing tooth are called abutment teeth, whereas the missing teeth in between are called pontics. Dental crowns and bridges are considered fixed prosthetic devices, unlike dentures, which you can take out and clean. Crowns and bridges are cemented onto abutment teeth or implants, and can only be removed by a dentist.
What are the benefits of dental bridges?
Dental bridges can:
- Restore your smile
- Replace a large part of a damaged tooth when a filling would damage it further
- Restore a natural appearance to teeth that have become discolored after a root canal treatment
- Restore the ability to properly chew and speak
- Distribute the forces in your bite properly by replacing missing teeth
- Stabilize teeth affected by parodontopathy, a disease which affects the tissues that support the teeth and which causes them to come loose, shift and finally fall out
If missing teeth are not replaced with dental bridges, this can lead to problems with your jaw joint due to its unnatural movements.
What type of dental bridges are available?
Traditional bridges are dental bridges in which abutment teeth adjoin the missing tooth. Cantilever bridges are used when there are no abutment teeth on one side of the missing tooth.
As for the materials used, bridges and crowns can be metal-free or metal-ceramic. Metal-ceramic crowns (bridges) can be traditional metal-ceramic bridges or they can be made from the combination of gold and ceramics, where porcelain is fused to a gold alloy substructure. The combination of gold and porcelain is the most expensive, but also the most durable one. Gold is an inert material, and therefore provides the best protection to the tooth it covers, which is the reason why cavities rarely appear under those bridges, even after many years of use.
How are dental bridges made?
After an oral examination, the dentist will examine your x-rays and then begin preparing your teeth and tissues that support them.
Preparation for this dental procedure entails:
- Removal of teeth which are so damaged that they cannot be repaired
- Removal of hard and soft dental deposits (such as plaque)
- Treatment of infected root canals
- Creating and cementing posts and cores which will ensure that these teeth look like they have been filed
How long does a dental bridge procedure take?
It usually takes a month after the tooth extraction for the bone defect (the socket at the tooth extraction site) to be completely filled with bone tissue. After these preparations, your dentist will begin recontouring your teeth.
Teeth recontouring (removal of a portion of enamel and dentin) allows room for a crown which will replace the missing part of the tooth and give it a natural appearance. After recontouring, impressions of the filed teeth are made (first with a high-density and then with low-density, more precise material) along with impressions of the teeth from the opposite jaw (antagonist teeth), which your dentist will then use to assess your bite alignment. Temporary crowns are usually made in this phase, especially if vital teeth (teeth with intact roots and canals) are present. The purpose of temporary crowns is to protect reshaped teeth and to ensure that patients can function normally while they are waiting for a permanent bridge. Next, impressions are sent to dental labs where a dental technician will make cast models of filed teeth and then use them to design bridges.
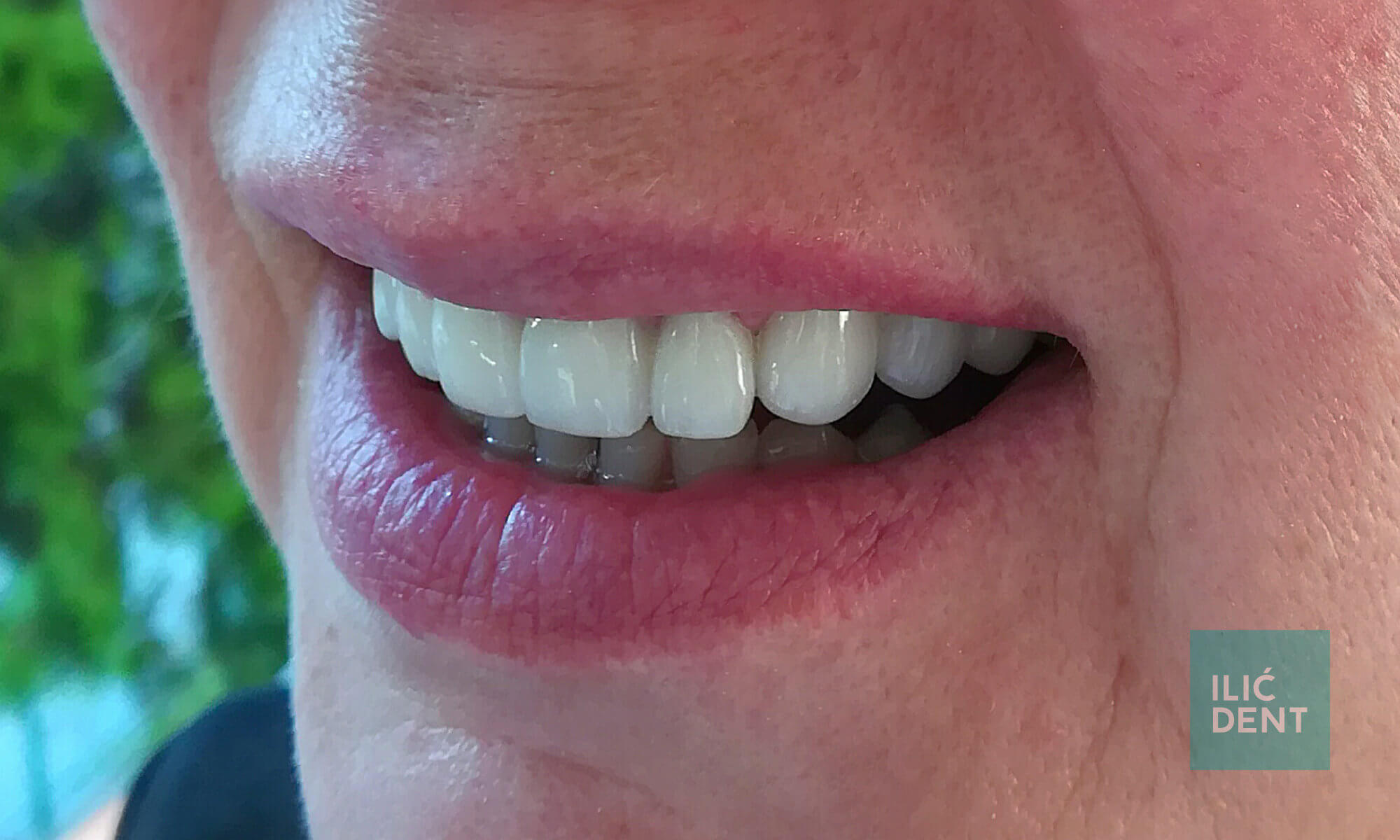
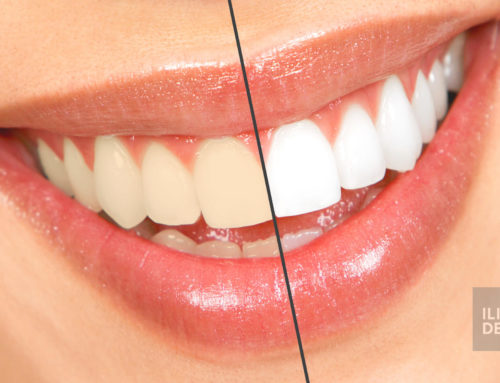
During the next visit, the temporary bridge is removed and the dentist will check the fit of the new bridge structure without the final porcelain layer (testing the fit of the metal structure in the case of metal-ceramic bridges, or the fit of the core in the case of metal-free bridges). In this phase, decisions on shade of teeth, i.e. of the future bridge (crown) is usually made, and both color decisions and shade matching should be done under natural light conditions. In the case of larger dental bridges, the patient can opt for a complete change of color. In this case, patients usually choose lighter shades so that their smile would be brighter, like so-called Hollywood smile. After this, your dentist will check the shape and shade of porcelain crowns and bite of your teeth, and at this stage, all other corrections can be decided upon. The bridge is then returned to the dental technician so that the details noted during the try-in can be modified. Next, bridges and crowns are glazed in order to achieve natural shine. If both the patient and the dentist are satisfied with the modifications, the bridge will be cemented. Your dentist may cement the bridge temporarily (until the patient becomes accustomed to the restoration) or permanently.
How much do dental bridges cost?
The total dental bridge cost includes the cost of all pontics and abutments. You can check all of our prices on our pricing page, whereas the price of bridges made of gold and ceramics depend on the weight of the bridge and the current gold rate, so be sure to inquire about the price of a specific bridge.
Will it be difficult to speak or eat with dental bridge?
After the initial adjustment phase, most patients quickly become accustomed to the bridge, and regain the ability to speak properly. Chewing with dental bridges is the same as chewing with your natural teeth. Avoid chewing hard and sticky foods, which should be avoided even if you have natural teeth. We recommend eating soft foods in the beginning, until you become accustomed to the bridge.
You can significantly prolong the longevity of your dental bridges by practicing good oral hygiene. This entails seeing your dentist regularly (to remove plaque) and using mouthwashes and water flossers in addition to brushing your teeth and flossing regularly. In any case, you should avoid chewing hard foods.
For all additional questions and consultation appointments, you reach us at phone +381 64 3411219 (Viber) or from our contact page.
Consultations are fee of charge!